PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
2392-39-4 (Sodium Phosphate)
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
AUTOIGNITION
NFPA RATINGS
REFRACTIVE INDEX
Stable under ordinary conditions
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS
- Glucocorticoid Receptor Agonists
- Dexamethasone
- Triamcinolone
- Hydrocortisone
- Prednisone
- Glucocorticoid Receptor Antagonists
- Mifepristone
- Onapristone
- Mineralocorticoid Receptor Agonists
- Aldosterone
- Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonists
- Spironolactone
- Eplerenone
Dexamethasone, a synthetic glucocorticoid of an analogue of cortisol, is therapeutically used in the replacement for adrenal insufficiency and to treat inflammatory, arthritis and certain forms of overactive immune response in a wide variety of disorders. It is used as an antiemetic in cancer chemotherapy. It counteracts the development of edema. It is also used as a diagnostic context in the detection of urinary levels of cortisol and 17-hydroxycorticosteroid. measured following administration of dexamethasone; cortisol secretion is suppressed in patients with Cushing's syndrome (glucocorticoid excess) but not in those with ectopic ACTH syndrome or adrenal tumors at 16 times the level used in replacement therapy; cortisol secretion is suppressed in normal patients but not in those with Cushing's syndrome at three to four times the level used in replacement therapy. The chemical designation is (11beta,16alpha)-9-fluoro-11,17,21-trihydroxy-16-methylpregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione. Some esters and salts of dexamethasone are administered by intraarticular, intravenous, or intramuscular injection, by inhalation, or applied to the skin and conjunctiva. Examples are as follows;
- Dexamethasone-17-acetate (CAS RN: 1177-87-3)
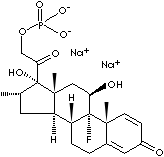
- Dexamethasone Disodium Phosphate (CAS RN: 2392-39-4)
- Dexamethasone Valerate (CAS RN: 14899-36-6)
- Dexamethasone-21-isonicotinate (CAS RN: 2265-64-7)
- Dexamethasone Palmitate (CAS RN: 33755-46-3)
- Dexamethasone Propionate (CAS RN: 55541-30-5)
- Dexamethasone Acefurate (CAS RN: 83880-70-0)
- Dexamethasone-21-galactoside (CAS RN: 92901-23-0)
APPEARANCE
IDENTIFICATION
Complies
ASSAY
OPTICAL ROTATION
+75° ~ +83°
pH
7.5 - 9.5
RELATED SUBSTANCE
Complies
FREE DEXAMETHASONE
1.0% max
FREE PHOSPHATE
1.0% max
ETHANOL
3.0% max
WATER
10.0% max